The sustainability module comprehensively addresses various dimensions of the term, effectively managing both the environmental and social sustainability aspects of production processes.
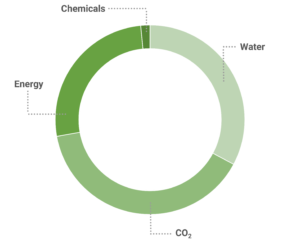
From an environmental standpoint, the module possesses the capability to amass data from heterogeneous sources, culminating in the establishment of the environmental impact of each phase of a product’s lifecycle. For instance, it can calculate this impact in terms of CO2 equivalence. These pivotal insights are harvested from a diverse array of origins, including third-party systems like SCADA and environmental monitoring setups, sensors provided by Antares Vision, or systems such as PLCs. In cases where direct data might be lacking, the module is endowed with the ability to employ models or leverage averaged data to estimate the impact of a particular activity. Furthermore, the module extends its influence to encompass the entire end-of-life phase of a product, considering the environmental consequences related to disposal and recycling.
Transitioning to the realm of social sustainability, the ecosystem adeptly intersects production data with existing contracts. This amalgamation facilitates the optimization of workloads and enables real-time alerts to supervisors should any non-compliance with guidelines arise. For instance, this functionality can prove indispensable in situations like combating exploitative labor practices, such as cases of worker exploitation (i.e. gangmastering) within the agricultural sector. By seamlessly merging production data and contractual parameters, the module contributes to fostering ethical and socially responsible production practices.
In essence, the sustainability module operates as a dynamic platform that empowers organizations to holistically evaluate and enhance their environmental and social footprints. Through its data-driven insights, it enables strategic decisions that align with sustainable goals, ensuring responsible practices and reinforcing corporate social responsibility.